Most Dangerous Hacker in the World: In the digital age, where the internet connects every aspect of our lives, cybersecurity has become a paramount concern. With the rise of cyber threats, one question looms large: Who is the most dangerous hacker in the world?
This article aims to explore this question by delving into the profiles of some of the world’s most notorious hackers, their methods, and the impact of their actions on global cybersecurity.
The Rise of Cybercrime
Before identifying the most dangerous hacker in the world, it’s crucial to understand the backdrop of cybercrime. The internet has revolutionized the way we communicate, work, and entertain ourselves, but it has also opened new avenues for criminal activities. From stealing personal information to disrupting critical infrastructure, cybercriminals have demonstrated an alarming ability to cause widespread damage.
Early Days of Hacking
The concept of hacking dates back to the 1960s when computer enthusiasts began exploring the capabilities of early computers. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s and 1990s that hacking evolved from a hobbyist pursuit to a serious criminal enterprise. The emergence of the internet provided hackers with a vast playground and an unprecedented number of potential targets.
Modern Cyber Threats
Today, cyber threats are more sophisticated and widespread than ever before. Hackers employ various techniques, including phishing, ransomware, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, to achieve their goals. As technology advances, so too do the methods used by these cybercriminals, making them a constant threat to individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
Most Dangerous Hacker in The World Throughout History
To determine the most dangerous hacker in the world, we must first examine some of the top hackers in the world who have left their mark on the cyber landscape.
Kevin Mitnick: The Original Hacker
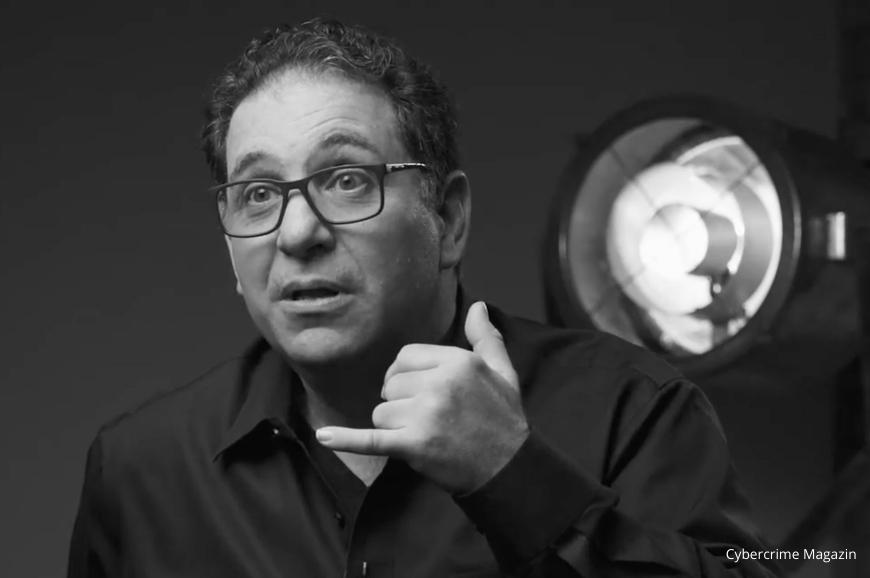

Kevin Mitnick, often dubbed the world’s most famous hacker, gained notoriety in the 1990s for his audacious exploits. His hacking career began at a young age, and he quickly became skilled at social engineering—manipulating people to gain access to confidential information. Mitnick’s most infamous hacks include breaking into the systems of major corporations like IBM, Nokia, and Motorola.
Mitnick’s actions landed him on the FBI’s Most Wanted list, and he was eventually arrested in 1995. After serving five years in prison, he reinvented himself as a cybersecurity consultant, using his knowledge to help organizations defend against cyber threats. While Mitnick’s activities were undoubtedly dangerous, they also highlighted the vulnerabilities in the emerging digital landscape.
Gary McKinnon: The NASA Hacker
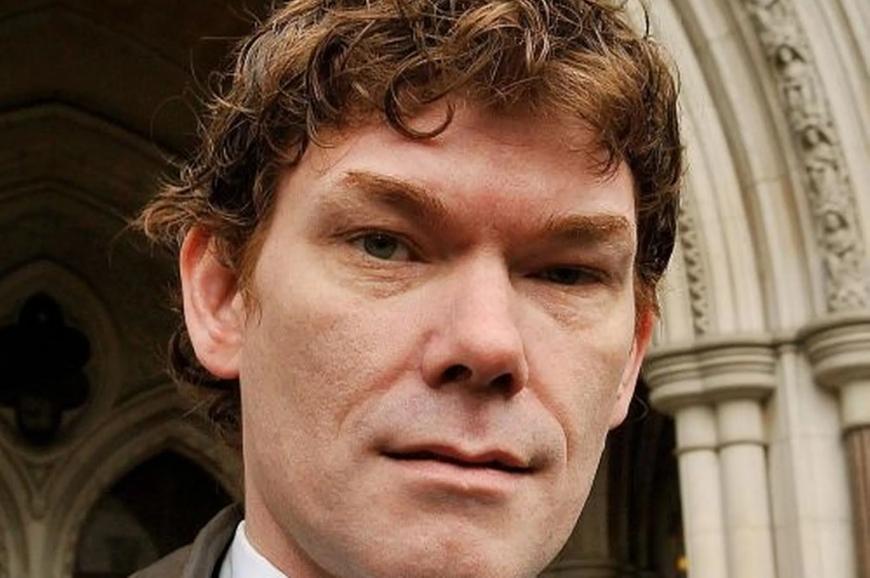

Gary McKinnon, a British hacker, became infamous for what has been described as the largest military computer hack of all time. Between 2001 and 2002, McKinnon gained unauthorized access to 97 U.S. military and NASA computers. He claimed his goal was to uncover evidence of UFOs and free energy suppression, but his actions caused significant disruptions and led to a costly cleanup.
McKinnon’s case sparked a lengthy legal battle over his extradition to the United States, which he ultimately avoided due to his medical condition. Despite his motives being less financially driven than other hackers, the scale and audacity of his activities underscore the potential for individual hackers to cause significant harm.
Albert Gonzalez: The Retail Cybercrime Kingpin
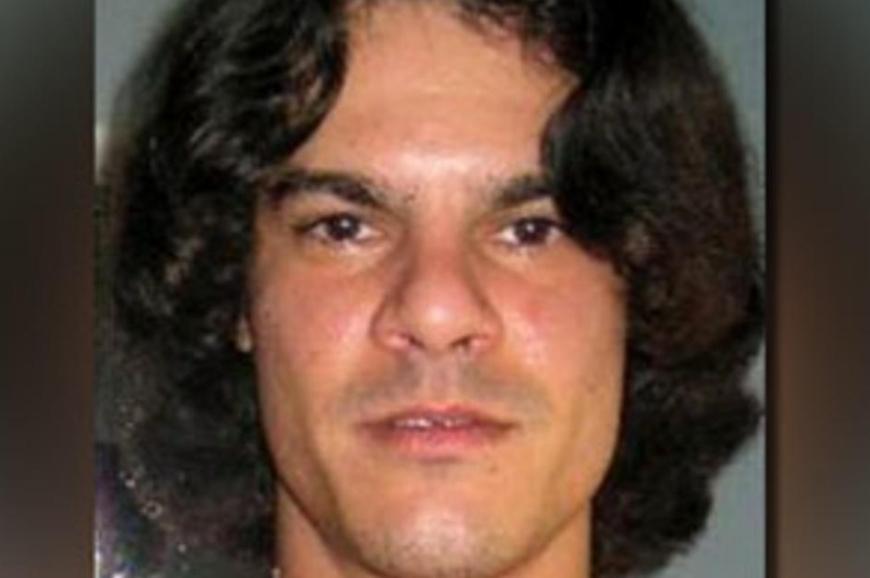

Albert Gonzalez is a name that strikes fear in the hearts of retail companies. Gonzalez orchestrated one of the largest and most sophisticated credit card fraud schemes in history. Between 2005 and 2007, he and his accomplices stole over 170 million credit card numbers from major retailers, including TJX Companies and Heartland Payment Systems.
Gonzalez’s methods were highly sophisticated, involving the use of SQL injection attacks to gain access to corporate networks and installing malware to capture card data. His actions resulted in millions of dollars in financial losses and demonstrated the vulnerabilities in payment processing systems. Gonzalez was eventually arrested and sentenced to 20 years in prison, but his legacy as one of the top hackers in the world endures.
Anonymous: The Collective of Hacktivists
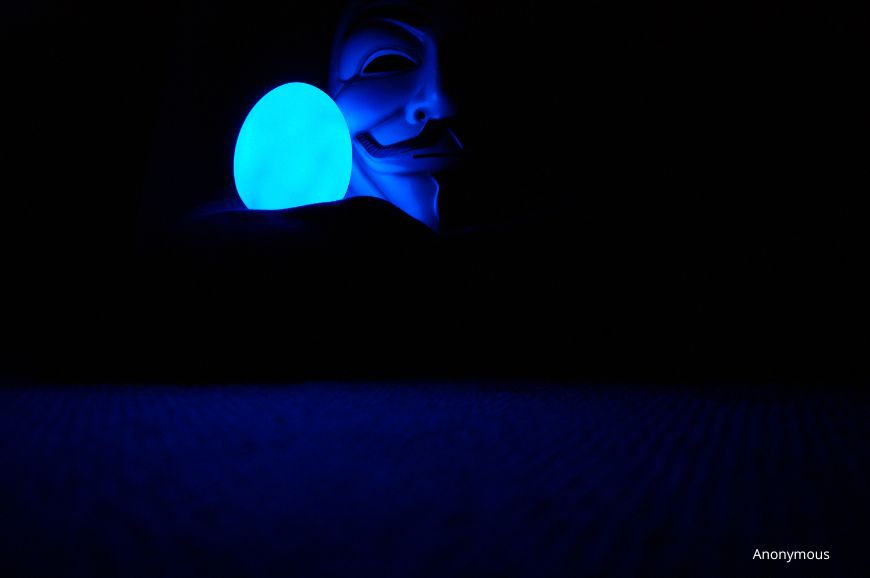

While not a single individual, the hacking collective known as Anonymous has made a significant impact on the cyber world. Emerging in the early 2000s, Anonymous is a decentralized group of hackers and activists who operate under the banner of promoting free speech and fighting against corruption.
Anonymous has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks, including DDoS attacks on government websites, corporations, and even terrorist organizations like ISIS. Their activities have brought attention to various social and political issues, but their methods and the legality of their actions have sparked controversy.
Explore the full list of the top 10 hackers in the world to see the other six most dangerous hackers in the world.
The Evolution of Cyber Threats
As technology continues to advance, so do the tactics and capabilities of hackers. The emergence of state-sponsored hacking and cyber warfare has added a new dimension to the threat landscape. These sophisticated operations are often carried out by nation-states seeking to gain political, economic, or military advantages.
State-Sponsored Hackers
One of the most significant developments in recent years is the rise of state-sponsored hacking groups. These groups, often backed by national governments, carry out highly sophisticated cyber attacks with the aim of espionage, sabotage, or disruption. Some of the notable examples include:
- Lazarus Group: Believed to be affiliated with North Korea, this group has been linked to numerous high-profile attacks, including the 2014 Sony Pictures hack and the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack.
- Fancy Bear: Associated with Russian intelligence, Fancy Bear has been implicated in a range of cyber espionage activities, including the hacking of the Democratic National Committee during the 2016 U.S. presidential election.
- APT10: A Chinese hacking group, APT10, has been involved in cyber espionage targeting a variety of industries worldwide, including aerospace, telecommunications, and healthcare.
These state-sponsored groups operate with significant resources and backing, making them formidable adversaries in the cyber realm.
The Rise of Ransomware
Ransomware has emerged as one of the most prevalent and destructive forms of cybercrime. This type of malware encrypts the victim’s data and demands a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. High-profile ransomware attacks, such as the WannaCry and NotPetya outbreaks, have caused widespread disruption and financial losses.
The profitability of ransomware has attracted organized crime groups, who operate ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) models, providing tools and infrastructure to other criminals in exchange for a cut of the profits. The anonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions has further fueled the growth of this cyber menace.
The Most Dangerous Hacker in the World: A Contender
Given the numerous notorious hackers throughout history and the evolving threat landscape, identifying a single individual as the most dangerous hacker in the world is a daunting task. However, one name that often surfaces in this discussion is Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev.
Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev: The Kingpin of Cybercrime
Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev, known by his online aliases “Slavik” and “lucky12345,” is a Russian cybercriminal responsible for some of the most damaging and sophisticated cyber attacks in history. Bogachev is the creator of the Zeus malware, which has been used to steal hundreds of millions of dollars from banks and financial institutions worldwide.
The Zeus Malware
Zeus is a type of Trojan horse malware that allows attackers to steal banking credentials by logging keystrokes and capturing screenshots. It first appeared in 2007 and quickly became one of the most notorious and widespread banking Trojans. Bogachev and his associates used Zeus to create a massive botnet, which they used to carry out a variety of criminal activities, including:
- Bank Fraud: Using stolen credentials to transfer money from victims’ bank accounts.
- Identity Theft: Harvesting personal information for sale on the dark web.
- Ransomware: Incorporating ransomware into the botnet to extort money from victims.
The Zeus botnet was highly resilient, employing advanced techniques to evade detection and takedown efforts by law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals.
GameOver Zeus
In 2011, Bogachev introduced an even more sophisticated version of Zeus known as GameOver Zeus. This variant used a peer-to-peer architecture, making it more difficult to disrupt. GameOver Zeus was responsible for a series of high-profile attacks, including a $6 million theft from a financial institution in North Carolina.
The Impact of Bogachev’s Actions
Bogachev’s activities have had a profound impact on the global financial system. The scale and sophistication of his operations have caused billions of dollars in losses and prompted significant investments in cybersecurity by financial institutions. Despite efforts by international law enforcement agencies, Bogachev remains at large, and his activities have set a high bar for other cyber criminals.
The Ongoing Threat
The legacy of Bogachev’s work continues to influence the cyber threat landscape. The techniques and tools he developed have been adopted and adapted by other cybercriminals, perpetuating the cycle of cybercrime. His ability to evade capture and continue operating underscores the challenges faced by law enforcement in combating cyber threats.
Tips for Individuals to Stay Safe Online
In the face of evolving cyber threats and the activities of the top hackers in the world, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their cybersecurity posture. Here are some practical tips to stay safe online:
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
- Create complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid using easily guessable information such as birthdays or common words.
- Use different passwords for different accounts to minimize the impact of a potential breach.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Whenever possible, enable 2FA on your accounts for an added layer of security.
- 2FA requires you to provide two forms of identification before accessing your account, typically something you know (password) and something you have (e.g., a code sent to your phone).
3. Keep Software Updated
- Regularly update your operating system, browsers, and applications to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Enable automatic updates where available to ensure you are always running the latest versions.
4. Be Cautious of Phishing Attempts
- Be wary of unsolicited emails, messages, or phone calls asking for personal information or directing you to click on suspicious links.
- Verify the authenticity of requests from companies or individuals by contacting them directly through official channels.
5. Use Secure Networks
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions (e.g., online banking) without using a virtual private network (VPN).
- Ensure your home Wi-Fi network is secured with a strong password and encryption.
6. Backup Important Data
- Regularly back up your data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service.
- In case of ransomware or other data loss incidents, having backups can help you recover without paying a ransom.
7. Educate Yourself and Others
- Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Educate family members, especially children and elderly relatives, about safe online behaviors and potential risks.
8. Use Security Software
- Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on your devices.
- Keep these programs updated to detect and protect against the latest threats.
9. Limit Personal Information Sharing
- Be cautious about sharing personal information on social media or other online platforms.
- Review privacy settings to control who can see your information and limit exposure to potential identity theft or scams.
10. Practice Cyber Hygiene
- Log out of accounts when not in use, especially on shared or public computers.
- Be mindful of what you download and install, as malicious software can be disguised as legitimate applications.
Follow these tips and stay vigilant, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cybercrime and the activities of dangerous hackers. Remember, cybersecurity is a shared responsibility, and taking proactive steps to protect yourself ultimately contributes to a safer online environment for everyone.
Conclusion
The title of the most dangerous hacker in the world or the world most dangerous hacker or dangerous hacker in the world is not one that can be easily awarded to a single individual. The evolving nature of cyber threats means that new contenders are constantly emerging. However, the impact and sophistication of Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev’s activities make him a strong contender for this dubious honor.
As we continue to rely more heavily on digital technologies, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated. The stories of the top hackers in the world like Kevin Mitnick, Gary McKinnon, Albert Gonzalez, and the members of Anonymous serve as reminders of the vulnerabilities that exist in our interconnected world. Meanwhile, state-sponsored hacking groups and the rise of ransomware illustrate the increasing complexity and scale of cyber threats.
We must learn from past incidents and anticipate future threats, so we can better protect ourselves in the ever-evolving battle against cybercrime. So, this was all about the most dangerous hacker in the world. I hope now you know about some of the top hackers in the world.
What are your thoughts? Don’t forget to mention any other hacker if you think I’ve not mentioned it in this post. Also, don’t forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues.